From Pain to Relief – Finding the Right Treatment for Osgood Schlatter Disease
Osgood Schlatter Disease (OSD) is a common condition that affects the knee, especially in children and adolescents. It is characterized by pain and swelling just below the knee cap, where the tendon from the thigh muscle attaches to the shinbone. This condition is most commonly seen in growing children and adolescents, and is particularly prevalent in athletes who participate in sports that involve running and jumping. The pain and discomfort caused by OSD can make it difficult for individuals to participate in physical activities and can negatively impact their quality of life.
The exact cause of OSD is not entirely understood, but it is believed to be related to growth spurts. As the body grows rapidly, the muscles and tendons may become stretched and strained. In addition, sports and physical activity can place additional stress on the knee, which can exacerbate the condition. Biomechanical factors, such as overpronation or flat feet, can also contribute to the development of OSD.
The good news is that OSD can be treated effectively with a combination of conservative and surgical treatments. The key to successful treatment for Osgood Schlatter Disease is early diagnosis, as well as a comprehensive treatment plan that includes rest, physical therapy, and medication as needed. In this article, we will explore the causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for Osgood Schlatter Disease, as well as strategies for preventing the condition.
Causes of Osgood Schlatter Disease
As mentioned earlier, the exact cause of Osgood Schlatter Disease (OSD) is not entirely clear, but it is thought to be related to growth spurts. During periods of rapid growth, the muscles and tendons in the knee can become stretched and strained, leading to inflammation and pain. This is especially true for the patellar tendon, which attaches the thigh muscle to the shinbone just below the knee cap.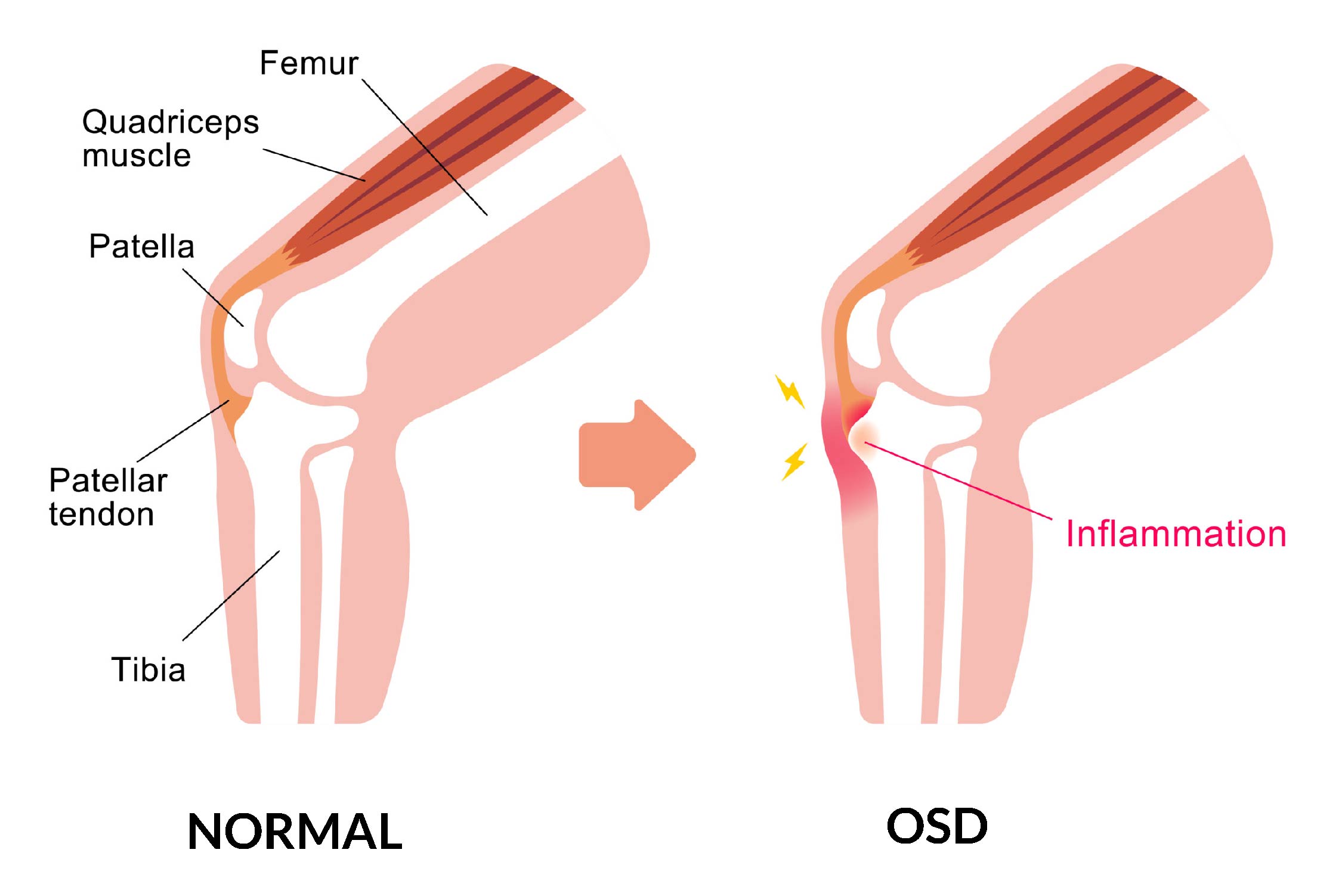
In addition to growth spurts, sports and physical activity can also play a role in the development of OSD. High-impact sports such as soccer, basketball, and gymnastics can put extra stress on the knee, leading to inflammation and pain. The repetitive motions involved in these sports can also aggravate the condition.
Another factor that may contribute to the development of OSD is biomechanical issues, such as overpronation or flat feet. When the foot overpronates or is flat, it can affect the alignment of the knee and place additional stress on the patellar tendon. This can lead to pain and inflammation in the area.
It’s also worth noting that OSD is more common in boys than girls, and the symptoms of OSD can be exacerbated by any muscle imbalance and poor quadriceps strength.
Overall, OSD is thought to be caused by a combination of factors, including growth spurts, sports and physical activity, and biomechanical issues. By understanding these causes, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk of developing OSD and get appropriate treatment if they do develop the condition.
Diagnosis of Osgood Schlatter Disease
Diagnosing Osgood Schlatter Disease (OSD) is usually done through a physical examination by a doctor. The doctor will ask about symptoms, medical history, and any activities that may have contributed to the development of OSD. They will also perform a physical examination of the knee, looking for signs of pain, swelling, and tenderness just below the knee cap.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor may also order an x-ray or MRI. These imaging tests can provide detailed pictures of the knee, which can help the doctor identify any changes in the bone or soft tissue that are characteristic of OSD.
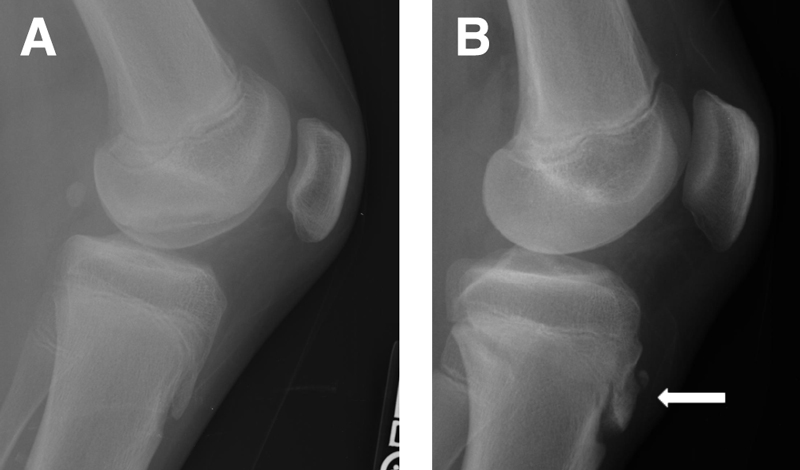
During the physical examination, doctor will also examine any other contributing factors. These factors include muscle imbalance, overpronation or flat feet, and quadriceps strength.
It’s important to note that OSD can sometimes be confused with other conditions that cause knee pain such as patellofemoral pain syndrome or chondromalacia patella. So, a proper diagnosis by a healthcare professional is necessary before starting any treatment.
Overall, a combination of a physical examination and imaging tests can provide an accurate diagnosis of OSD, which is crucial for effective treatment. With a proper diagnosis, individuals can receive the care and treatment they need to manage their symptoms and reduce their risk of complications.
Conservative treatment for Osgood Schlatter Disease
The primary goal of conservative treatment for Osgood Schlatter Disease (OSD) is to reduce pain and inflammation, and to promote healing. There are several treatment options that can be effective in managing the symptoms of OSD.
- Rest and activity modification: One of the most important things you can do to reduce pain and inflammation is to reduce the amount of stress on the knee. This may involve avoiding activities that are causing pain or discomfort and engaging in low-impact activities such as cycling or swimming instead.
- Stretching and strengthening exercises: Physical therapy can be an effective treatment for OSD. Stretching exercises can help to improve flexibility and range of motion in the knee, while strengthening exercises can help to improve muscle balance and support the knee.
- Cold therapy or cryotherapy: Applying cold to the knee can help to reduce inflammation and pain. Cold therapy can be done by using a reusable ice pack, or ice massage over the knee. Cryotherapy uses cryogenic temperatures to reduce pain and inflammation, it’s an effective method to reduce the pain and inflammation of OSD.
- Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen can help to reduce pain and inflammation. These medications can be taken as needed, but it’s important to follow the dosage instructions and not to take them for extended periods of time without consulting a healthcare professional.

It’s important to note that conservative treatment for OSD may not be enough to manage the symptoms in severe cases. In these cases, surgical options may be considered. But for most people, with proper diagnosis, treatment, and management, individuals can effectively reduce pain and inflammation, and promote healing.
Surgical treatment for Osgood Schlatter Disease
In severe cases of Osgood Schlatter Disease (OSD) where conservative treatment options have not been effective, surgery may be recommended. However, surgery is typically only considered as a last resort and after all the conservative options have been exhausted.
The surgical procedure used for OSD is called a patellectomy. This procedure involves removing the bony prominence, or lump, at the site of the pain and inflammation. This can help to reduce pain and improve function in the knee.
Recovery from surgery can take several months, and individuals will need to avoid putting weight on the knee while it heals. Physical therapy will be needed to regain strength, flexibility, and motion in the knee.
The outcomes of surgery for OSD are generally good, but this will depend on the stage of the disease at the time of surgery and how well the patient follows post-operative guidelines.
It’s important to note that surgery should only be considered as a last resort, after all the conservative options have been exhausted and in cases where the symptoms are severe and debilitating.
It’s important to have realistic expectations from surgery and to understand the recovery process. It can take several months before returning to sports and normal activities. Consultation with a doctor or an orthopedic surgeon is necessary to evaluate whether surgery is the best option for an individual case or not.
Prevention of Osgood Schlatter Disease
Preventing the development of Osgood Schlatter Disease (OSD) is crucial for reducing the risk of pain and discomfort in the knee. There are several strategies that can be effective in preventing OSD.
Proper stretching and exercise: Stretching and exercising can help to improve muscle balance and support the knee, reducing the risk of injury. Targeting the quadriceps, hamstrings and calf muscles can help to keep the knee in a neutral position and reduce the strain on the patellar tendon.
Maintaining a healthy body weight: Excess weight can place additional stress on the knee, increasing the risk of injury. Maintaining a healthy body weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help to reduce the risk of OSD.
Proper warm-up and cool-down: Proper warm-up and cool-down before and after physical activity can help to reduce the risk of injury. A warm-up can prepare the muscles for activity and a cool-down can help to reduce muscle soreness and stiffness.

Wearing supportive and well-fitting shoes: Wearing shoes that fit properly and provide adequate support can help to reduce the risk of injury. Shoes that are worn out or do not fit properly can increase the risk of OSD.
Avoiding activities that cause pain: Activities that cause pain should be avoided as they can worsen the condition. Individuals should look for activities that are less stressful on the knee or a combination of low-impact activities such as swimming, cycling or yoga.
It’s worth noting that prevention of OSD is essential in order to avoid the need of treatment, and to have a better quality of life. By following these strategies, individuals can reduce their risk of developing OSD and enjoy a more active, pain-free lifestyle.
Conclusion
Osgood Schlatter Disease (OSD) is a common condition that affects the knee, especially in children and adolescents. It is characterized by pain and swelling just below the knee cap, caused by the strain on the patellar tendon. This condition is most commonly seen in growing children and adolescents, and is particularly prevalent in athletes who participate in sports that involve running and jumping.
The exact cause of OSD is not entirely understood, but it is believed to be related to growth spurts, sports and physical activity and biomechanical issues.
Treatment for OSD includes a combination of conservative and surgical options. Conservative treatment includes rest and activity modification, stretching and strengthening exercises, cold therapy, and medication such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). In severe cases, surgery may be considered.
Preventing the development of OSD is crucial for reducing the risk of pain and discomfort in the knee. Strategies for preventing OSD include proper stretching and exercise, maintaining a healthy body weight, proper warm-up and cool-down, wearing supportive and well-fitting shoes and avoiding activities that cause pain.
In conclusion, OSD is a common and treatable condition that affects the knee. With proper diagnosis, treatment and management, individuals can effectively reduce pain and inflammation, and promote healing. Prevention is key, and by following the prevention strategies, individuals can reduce the risk of developing OSD and enjoy a more active, pain-free lifestyle.

